How to Authenticate Users with MetaMask using Angular
Introduction
This tutorial demonstrates how to create an Angular application that allows users to log in using their Web3 wallets.
After Web3 wallet authentication, the server creates a session cookie with a signed JWT stored inside. It contains session info (such as an address, signed message) in the user's browser.
Once the user is logged in, they will be able to visit a page that displays all their user data.
Prerequisites
- Follow the Your First Dapp - Angular tutorial to set up your Angular dapp and server
Install the Required Dependencies
To implement authentication using a Web3 wallet (e.g., MetaMask), we will use a Web3 library. For the tutorial, we will use @wagmi/core.
- Install
@wagmi/core,ethers, andaxiosdependencies -@wagmi/core@0.5.8is a stable version we can use with Angular 14:
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install @wagmi/core@0.5.8 ethers@^5 axios
yarn add @wagmi/core@0.5.8 ethers@^5 axios
pnpm add @wagmi/core@0.5.8 ethers@^5 axios
- Open
src/environments/environment.ts- add a variable ofSERVER_URLfor our server.
export const environment = {
production: false,
SERVER_URL: "http://localhost:3000",
};
- We will generate two components (pages) -
/signin(to authenticate) and/user(to show the user profile):
ng generate component signin
ng generate component user
- Open
src/app/app-routing.module.ts, add these two components as routes:
import { SigninComponent } from "./signin/signin.component";
import { UserComponent } from "./user/user.component";
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: "signin", component: SigninComponent },
{ path: "user", component: UserComponent },
];
Initial Setup
We will do an initial setup of our /signin and /user pages to make sure they work before integrating with our server.
- Open
src/app/signin/signin.component.htmland replace the contents with:
<h3>Web3 Authentication</h3>
<button type="button" (click)="handleAuth()">Authenticate via MetaMask</button>
- Open
src/app/signin/signin.component.tsand add an emptyhandleAuthfunction belowngOnInit(): void {}:
ngOnInit(): void {}
async handleAuth() {}
- Run
npm run startand openhttp://localhost:4200/signinin your browser. It should look like:
- Open
src/app/user/user.component.htmland replace the contents with:
<div *ngIf="session">
<h3>User session:</h3>
<pre>{{ session }}</pre>
<button type="button" (click)="signOut()">Sign out</button>
</div>
- Open
src/app/user/user.component.tsand add the variable we used above and an emptysignOut()function:
session = '';
ngOnInit(): void {}
async signOut() {}
- Open
http://localhost:4200/userin your browser. It should look like:
Server Setup
Now we will update our server's index.js for the code we need for authentication. In this demo, cookies will be used for the user data.
- Install the required dependencies for our server:
npm install cookie-parser jsonwebtoken dotenv
- Create a file called
.envin your server's root directory (wherepackage.jsonis):
- APP_DOMAIN: RFC 4501 DNS authority that is requesting the signing.
- MORALIS_API_KEY: You can get it here.
- ANGULAR_URL: Your app address. By default Angular uses
http://localhost:4200. - AUTH_SECRET: Used for signing JWT tokens of users. You can put any value here or generate it on
https://generate-secret.now.sh/32. Here's an.envexample:
APP_DOMAIN=amazing.finance
MORALIS_API_KEY=xxxx
ANGULAR_URL=http://localhost:4200
AUTH_SECRET=1234
- Open
index.js. We will create a/request-messageendpoint for making requests toMoralis.Authto generate a unique message (Angular will use this endpoint on the/signinpage):
// to use our .env variables
require("dotenv").config();
// for our server's method of setting a user session
const cookieParser = require("cookie-parser");
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const config = {
domain: process.env.APP_DOMAIN,
statement: "Please sign this message to confirm your identity.",
uri: process.env.ANGULAR_URL,
timeout: 60,
};
app.post("/request-message", async (req, res) => {
const { address, chain, network } = req.body;
try {
const message = await Moralis.Auth.requestMessage({
address,
chain,
network,
...config,
});
res.status(200).json(message);
} catch (error) {
res.status(400).json({ error: error.message });
console.error(error);
}
});
- We will create a
/verifyendpoint for verifying the signed message from the user. After the user successfully verifies, they will be redirected to the/userpage where their info will be displayed.
app.post("/verify", async (req, res) => {
try {
const { message, signature } = req.body;
const { address, profileId } = (
await Moralis.Auth.verify({
message,
signature,
networkType: "evm",
})
).raw;
const user = { address, profileId, signature };
// create JWT token
const token = jwt.sign(user, process.env.AUTH_SECRET);
// set JWT cookie
res.cookie("jwt", token, {
httpOnly: true,
});
res.status(200).json(user);
} catch (error) {
res.status(400).json({ error: error.message });
console.error(error);
}
});
- We will create an
/authenticateendpoint for checking the JWT cookie we previously set to allow the user access to the/userpage:
app.get("/authenticate", async (req, res) => {
const token = req.cookies.jwt;
if (!token) return res.sendStatus(403); // if the user did not send a jwt token, they are unauthorized
try {
const data = jwt.verify(token, process.env.AUTH_SECRET);
res.json(data);
} catch {
return res.sendStatus(403);
}
});
- Lastly we will create a
/logoutendpoint for removing the cookie.
app.get("/logout", async (req, res) => {
try {
res.clearCookie("jwt");
return res.sendStatus(200);
} catch {
return res.sendStatus(403);
}
});
Your final index.js should look like this:
const Moralis = require("moralis").default;
const express = require("express");
const cors = require("cors");
const cookieParser = require("cookie-parser");
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
require("dotenv").config();
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.use(express.json());
app.use(cookieParser());
// allow access to Angular app domain
app.use(
cors({
origin: process.env.ANGULAR_URL,
credentials: true,
})
);
const config = {
domain: process.env.APP_DOMAIN,
statement: "Please sign this message to confirm your identity.",
uri: process.env.ANGULAR_URL,
timeout: 60,
};
// request message to be signed by client
app.post("/request-message", async (req, res) => {
const { address, chain, network } = req.body;
try {
const message = await Moralis.Auth.requestMessage({
address,
chain,
network,
...config,
});
res.status(200).json(message);
} catch (error) {
res.status(400).json({ error: error.message });
console.error(error);
}
});
// verify message signed by client
app.post("/verify", async (req, res) => {
try {
const { message, signature } = req.body;
const { address, profileId } = (
await Moralis.Auth.verify({
message,
signature,
networkType: "evm",
})
).raw;
const user = { address, profileId, signature };
// create JWT token
const token = jwt.sign(user, process.env.AUTH_SECRET);
// set JWT cookie
res.cookie("jwt", token, {
httpOnly: true,
});
res.status(200).json(user);
} catch (error) {
res.status(400).json({ error: error.message });
console.error(error);
}
});
// verify JWT cookie to allow access
app.get("/authenticate", async (req, res) => {
const token = req.cookies.jwt;
if (!token) return res.sendStatus(403); // if the user did not send a jwt token, they are unauthorized
try {
const data = jwt.verify(token, process.env.AUTH_SECRET);
res.json(data);
} catch {
return res.sendStatus(403);
}
});
// remove JWT cookie
app.get("/logout", async (req, res) => {
try {
res.clearCookie("jwt");
return res.sendStatus(200);
} catch {
return res.sendStatus(403);
}
});
const startServer = async () => {
await Moralis.start({
apiKey: process.env.MORALIS_API_KEY,
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`);
});
};
startServer();
- Run
npm run startto make sure your server runs without immediate errors.
Bringing It All Together
Now we will finish setting up our Angular pages to integrate with our server.
- Open
src/app/signin/signin.component.ts. Add our required imports:
// for navigating to other routes
import { Router } from "@angular/router";
// for making HTTP requests
import axios from "axios";
import { getDefaultProvider } from "ethers";
import {
createClient,
connect,
disconnect,
getAccount,
signMessage,
InjectedConnector,
} from "@wagmi/core";
import { environment } from "../../environments/environment";
- Add this code to set up the Wagmi client:
const client = createClient({
autoConnect: true,
provider: getDefaultProvider(),
});
- Replace our empty
handleAuth()function with the following:
async handleAuth() {
const { isConnected } = getAccount();
if (isConnected) await disconnect(); //disconnects the web3 provider if it's already active
const provider = await connect({ connector: new InjectedConnector() }); // enabling the web3 provider metamask
const userData = {
address: provider.account,
chain: provider.chain.id,
network: 'evm',
};
const { data } = await axios.post(
`${environment.SERVER_URL}/request-message`,
userData
);
const message = data.message;
const signature = await signMessage({ message });
await axios.post(
`${environment.SERVER_URL}/verify`,
{
message,
signature,
},
{ withCredentials: true } // set cookie from Express server
);
// redirect to /user
this.router.navigateByUrl('/user');
}
- Open
src/app/user/user.component.ts. Add our required imports:
import { Router } from "@angular/router";
import axios from "axios";
import { environment } from "../../environments/environment";
- Replace
ngOnInit(): void {}with:
async ngOnInit() {
try {
const { data } = await axios.get(
`${environment.SERVER_URL}/authenticate`,
{
withCredentials: true,
}
);
const { iat, ...authData } = data; // remove unimportant iat value
this.session = JSON.stringify(authData, null, 2); // format to be displayed nicely
} catch (err) {
// if user does not have a "session" token, redirect to /signin
this.router.navigateByUrl('/signin');
}
}
- Replace our empty
signOut()function with the following:
async signOut() {
await axios.get(`${environment.SERVER_URL}/logout`, {
withCredentials: true,
});
this.router.navigateByUrl('/signin');
}
If you get errors related to default imports, open your tsconfig.app.json file and add "allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true under compilerOptions:
"compilerOptions": {
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true,
"outDir": "./out-tsc/app",
"types": []
}
Testing the MetaMask Wallet Connector
Visit http://localhost:4200/signin to test the authentication.
- Click on the
Authenticate via MetaMaskbutton:
- Connect the MetaMask wallet and sign the message:
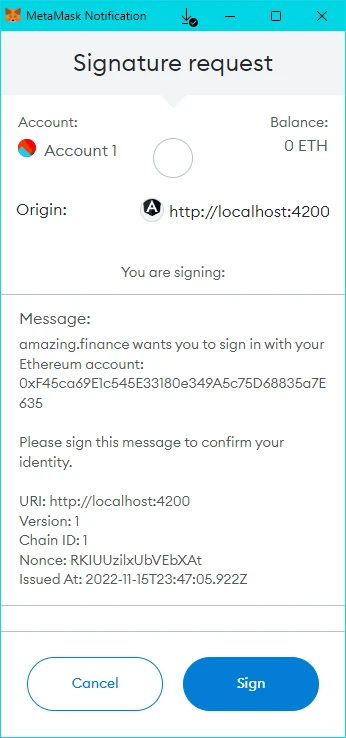
- After successful authentication, you will be redirected to the
/userpage:
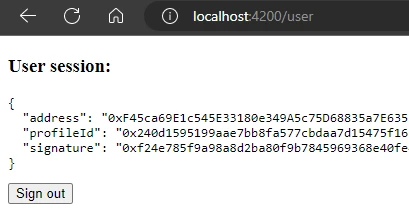
- When a user authenticates, we show the user's info on the page.
- When a user is not authenticated, we redirect to the
/signinpage. - When a user is authenticated, we show the user's info on the page, even refreshing after the page.